
- Renderman tutorial normal maps hypershade how to#
- Renderman tutorial normal maps hypershade software#
Maya is parts! Everything you ever create in Maya is a node. Although this tutorial everything is quite detailed, and describes each step, you have to be initial skills in Maya, the concept of the material editor and Hypershade nodes.
Renderman tutorial normal maps hypershade how to#
This lesson we will look at some simple nodes in Maya, the material editor Hypershade and finally learn how to use the site Multiply-Divide node multiplication-division in order to control the intensity and depth maps of displacement displacement map. On the other hand, a low value could result in a clipping of the displaced mesh.In this lesson we will look at some simple nodes in Mayathe material editor Hypershade and finally learn how to use the site Multiply-Divide multiplication-division unit to control the intensity and depth maps of displacement displacement map. When the bounding box is hit first by a ray, the displacement will be computed, so an unnecessarily high value will decrease the rendering efficiency. Padding defines how much to extend the bounding box of the object so that it can include any additional displacement coming from the displacement shader.
You can use this value to compensate for any inconsistencies between the exported displacement map and the low-resolution geometry. This attribute only applies with normal displacement. Displacement height can have either positive or negative values. Same displacement shader assigned to two meshes, however, the mesh on the right has a per-object Height of 2. Another example would be an object that has more than one shader but requires two different Height values such as in the example below. This may be useful in a scene that has two objects with the same shader but requires different shape displacement values. This means that any changes to the displacement that are made on a mesh will modify the default displacement shader attributes. As well as the Displacement Shader, MtoA also has displacement options on a per-object basis. Autobump poses the same problem as with padding, and so Arnold enables it if at least one of the displacement shaders has it enabled.
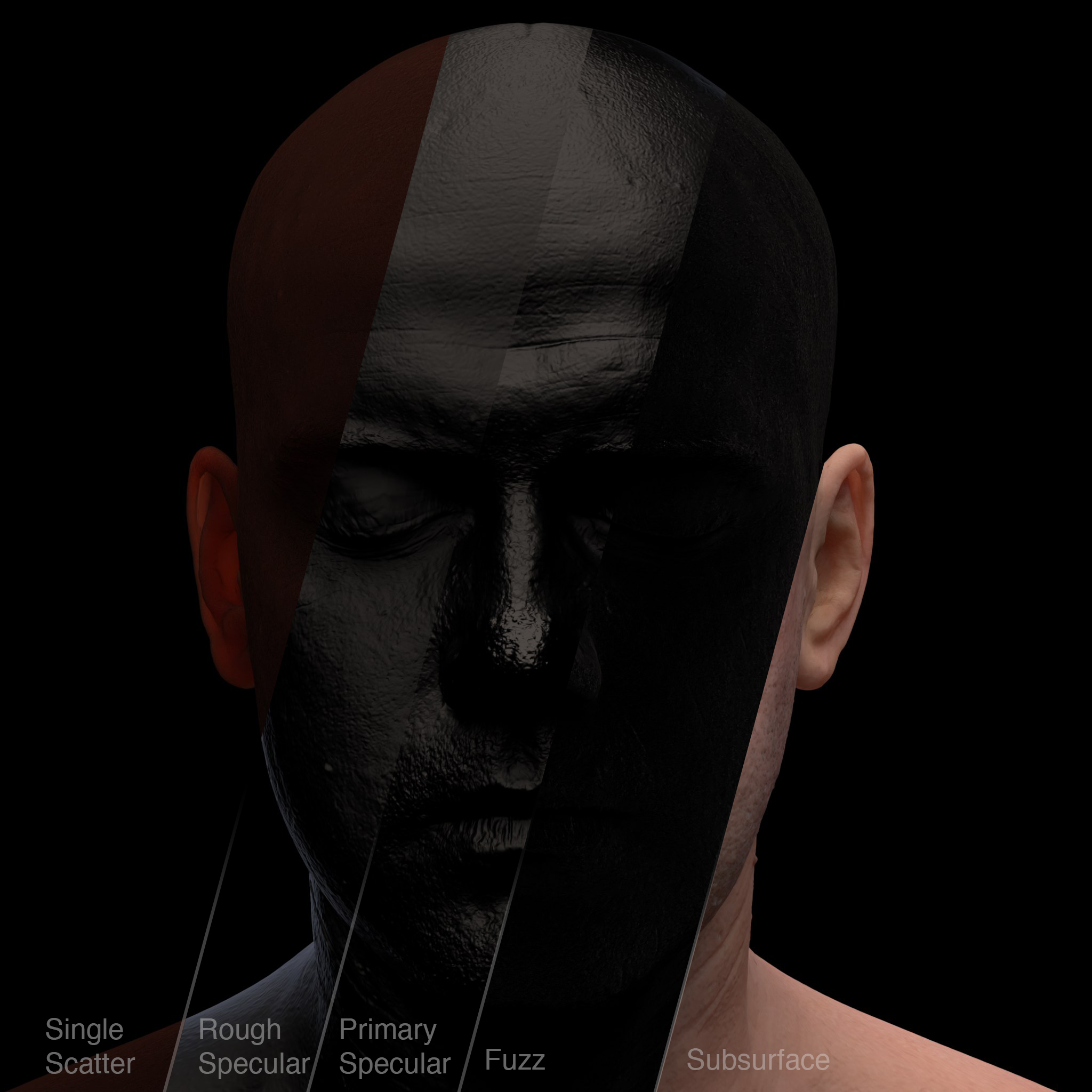

With multiple displacement shaders per object, and since an object can only have one value of Bounds Padding, Arnold takes the maximum value from all of them. However, any values that are entered in the Arnold attributes of the displacement node will override those settings. It is possible to set displacement settings on a per-face or per-object basis.
Renderman tutorial normal maps hypershade software#
This is a better choice compared to increasing the subdivisions of the mesh within the DCC software which will send the tessellated geometry to the renderer. Organisational behaviour past exam papers with answers This subdivision happens at render time, whenever a ray hits the bound box of the object. You must be careful when increasing the number of subdivision iterations each iteration quadruples the geometry. Subdivision Iterations: 2 Subdivision Iterations: 4 Subdivision Iterations: 8 Changing the Subdivision Type to either Catclark or Linear subdivision rules and increasing the iterations will improve the displacement quality. The Displacement node must be connected to the displacement attribute of the shading group of the material that is assigned to the mesh that requires displacement.Īlways ensure that you use the highest quality texture maps for displacement mapping.

This is because integer formats do not support negative pixel values, which are used by floating-point displacement maps. An integer format will not work correctly. Make sure that you use a bit or bit floating-point format to store your image, and not an integer format. You should ensure that your base mesh geometry has a sufficient number of polygons otherwise subtle differences can occur between the displaced low-resolution geometry and the high-resolution mesh from which it was generated. The example above shows how a simple plane, with the addition of a displacement map, can produce an interesting looking simple scene. Displacement mapping differs from bump mapping in that it alters the geometry, and therefore will have a correct silhouette, and self-shadowing effects. Displacement maps can be an excellent tool for adding surface detail that would take far too long using regular modeling methods. Displacement texture map from JSplacement Roll over image to view without displacement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
